Erectile resumption
The Economist
 A mirror of prosperity
A mirror of prosperityICON BRICKELL, a three-tower complex in Miami’s financial district, was supposed to be a flagship project for the Related Group, the city’s top condominium developer. It would boast 1,646 luxury condos, a 91-metre-long pool, and a hundred 22-foot columns in its entryway. By 2010, however, it had become a symbol of the excesses of the city’s building boom, and Related was forced to hand two of the towers to its banks. Miami condo prices plunged to 60% below their peak. The vacancy rate jumped to 60%. Predictions flew that the market, the epicentre of America’s property crash, would take ten years to come back, or even longer.
The speed of the recovery has surprised everyone. Condo prices are already back near peak levels in Miami’s most desirable areas, and at 75-80% elsewhere. The available supply of units has fallen back to within the six-to-nine-months-of-sales range considered normal, from a stomach-churning 40 in 2008. Only 3% of condos are unoccupied. Sales of condos and single-family homes are above pre-crisis levels across Miami-Dade County. Commercial property, too, has rebounded, with demand outstripping supply. Developers are once again relaxed enough to crack jokes. “I call the current expansion the Viagra cycle,” jokes Carlos Rosso, Related’s president of condominium development. “We just want it to last a little longer.”
The recovery has been partly driven by low interest rates and bottom-fishing by private equity, which helped to clear excess inventory. But the biggest factor is that the city nicknamed the “Capital of Latin America” has attracted a flood of capital from Latin America. Rich people in turbulent spots such as Venezuela and Argentina are seeking a safe haven for their savings.
Estate agents are also seeing capital flight from within the United States. Individuals pay no state or city income tax in Miami, unlike, say, New York, whose mayor wants to hike taxes on the rich further. “Somebody said to me, ‘Give me three reasons why this will continue.’ My answer was: Maduro, Kirchner and De Blasio,” chuckles Marc Sarnoff, a Miami city commissioner, referring to the leaders of the capitalist-bashing regimes in Venezuela, Argentina and New York.
Another attraction is the 40% rise in Miami condo rents since 2009, buoying the income of owners who choose not to live in the tropical hurly-burly that Dave Barry, a local author, calls “Insane City”. Brokers report increased business from Eastern Europe and the Middle East (Qatar Airways will fly direct to Miami from June), and an uptick in inquiries from Chinese buyers.
Is another bubble forming already? Developers say this time is different, and in some ways it is. In a few years Miami has gone from the most- to the least-leveraged property market in America. Buyers of new condos typically have to put 50% down, half of that before building starts. Banks are loth to extend construction loans unless 60-75% of the units are already sold. In both residential and commercial projects, they require developers to put in much more equity than before. Mr Rosso says Related now puts in three times as much, which limits its ambition. The firm now has 2,000 condos in the works, a tenth of what it was building in 2007.
Still, a supply glut is possible. With developers gung-ho again, around 50 towers are under construction or planned in downtown Miami (including the Porsche Design Tower, whose well-heeled inhabitants will be able to take their cars up to the level on which they live in a special lift—this is useful if you really love your car). More were added last month when Oleg Baybakov, a Russian mining-to-property oligarch, bought a trio of condo-development sites for $30m, more than triple their assessed market value in 2013.
Miami’s developers are adept at using “smoke and mirrors” to hide the true number of pre-sold units, says Peter Zalewski of Condo Vultures, a property-intelligence firm. Some see the first signs of trouble. The stock of unsold condos and houses has crept up slightly since last summer. A local broker says that Blackstone, a private-equity firm with a taste for bricks and mortar, bought $120m of properties with his firm’s help in 2013 but “won’t do anything like that this year”. Mr Zalewski says banks are competing harder to finance certain projects, but this may not be a sign of unadulterated bullishness. They may simply be betting that many of the 134 towers proposed but not yet under construction in South Florida won’t get built—meaning the 57 that have already broken ground will do better than forecast.
Much will depend on whether Latin Americans remain addicted to Miami property and, should their ardour cool, whether Americans and others would take up the slack. Few domestic buyers are comfortable putting 50% down, especially when most of it is at risk if the project fails. One or two developers have begun to accept 30% down, a possible sign of increased reliance on home-grown buyers.
The market should get a fillip from the current and planned redevelopment of several chunks of downtown Miami. One of the most ambitious projects is Miami Worldcenter, a 30-acre retail, hotel and convention-centre complex that will feature Bloomingdale’s, Macy’s and a giant Marriott hotel. A science museum will soon join the art museum .
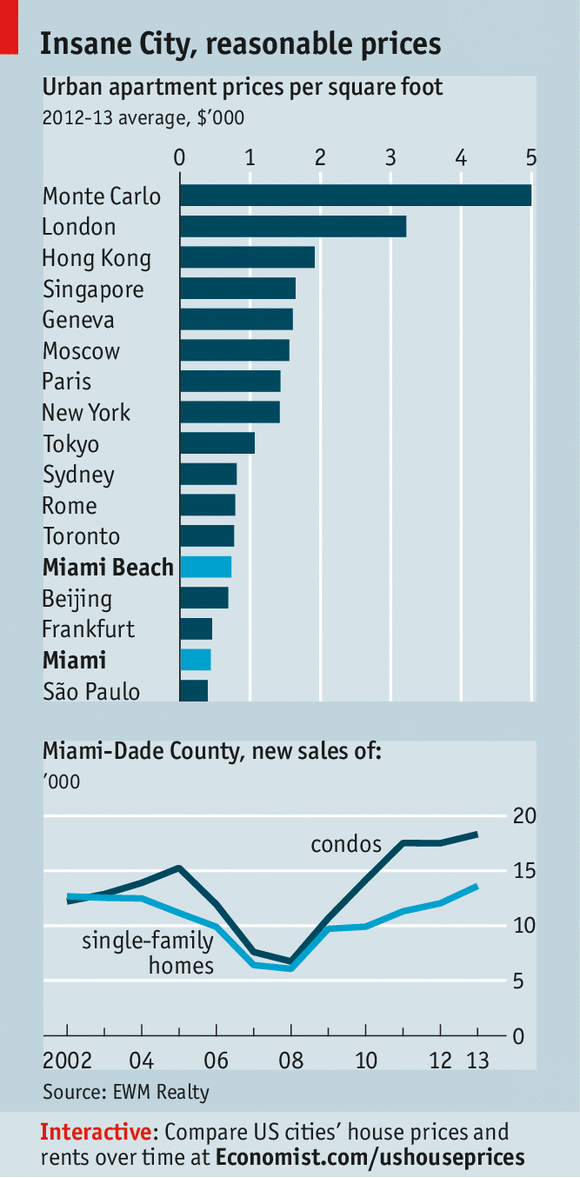
These projects build on progress made over the past decade towards becoming a world-class city, from the opening of dozens of top-notch restaurants to Art Basel picking Miami as one of the three venues for its shows (“the Super Bowl of the Art World”, as Tom Wolfe called it in his Miami novel, “Back to Blood”). Tourism is at record levels. Miami is the only American city besides New York in the top ten of Knight Frank’s 2014 global-cities index, which ranks cities by their attractiveness to the ultra-wealthy. (It comes seventh, ahead of Paris.) Property is still far cheaper than in most other cities on the list (see chart).
Miami’s Downtown Development Authority (DDA) is dangling the city’s low taxes and lovely weather in front of companies to persuade them to move there. This is starting to bear fruit, especially in finance: Universa, a $6 billion hedge fund in California, recently agreed to relocate, following part of Eddie Lampert’s ESL. SABMiller, a giant brewer, has moved its Latin American head office from Colombia. .
“I lived a long time in New York, but here [in Miami] it’s easier to make something from nothing,” enthuses Nitin Motwani, a DDA board member, who talks of the city’s skyline one day resembling Manhattan’s. Mr Zalewski is more cautious. Miami’s property market is “a great game”, he says, but “all it would take to send a chill through the entire market is one big project to go sideways.” Developers who joke about Viagra should keep some aspirin within reach, just in case.
Back to Blog